- Introduction to the machine used for weaving
: History and modern context - Technological Advancements: From Handlooms to Automatic Machines
- Comparing Leading Manufacturers: Global Market Analysis
- Custom Solutions: Tailoring Weaving Machines to Industry Needs
- Applications and Real-World Case Studies
- Performance Metrics: A Data-Driven Overview of Weaving Efficiency
- Conclusion: The Enduring Role of the Machine Used for Weaving

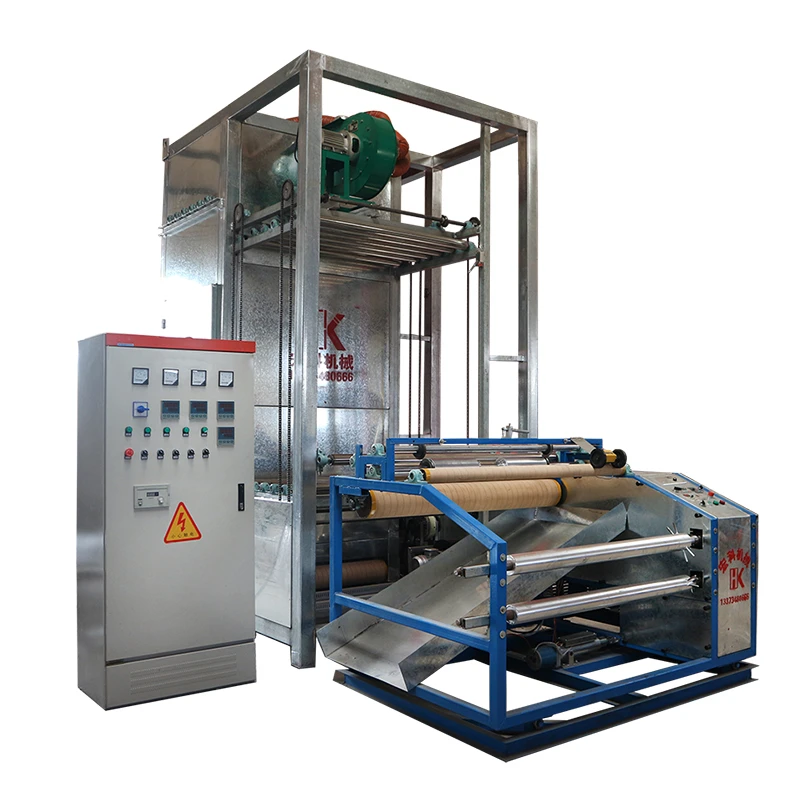
(the machine used for weaving)
Introduction: The Machine Used for Weaving Through the Ages
The machine used for weaving has continually evolved, bridging tradition and technology. Weaving, the interlacing of warp and weft to produce fabric, dates back thousand years but the mechanisms have changed remarkably. In the earliest civilizations, weaving was entirely manual, but the Industrial Revolution propelled it into the era of mechanization. Today, businesses and entrepreneurs face the challenge of choosing which machine is used for weaving that aligns with scalability, efficiency, and innovation. Recognizing the fundamental role of mechanized weaving in textiles, this overview details the journey from handlooms to advanced automatic looms and digital weaving solutions, setting the stage for critical comparisons, customization, and real-world impact.
Technological Advancements: From Handlooms to Automatic Machines
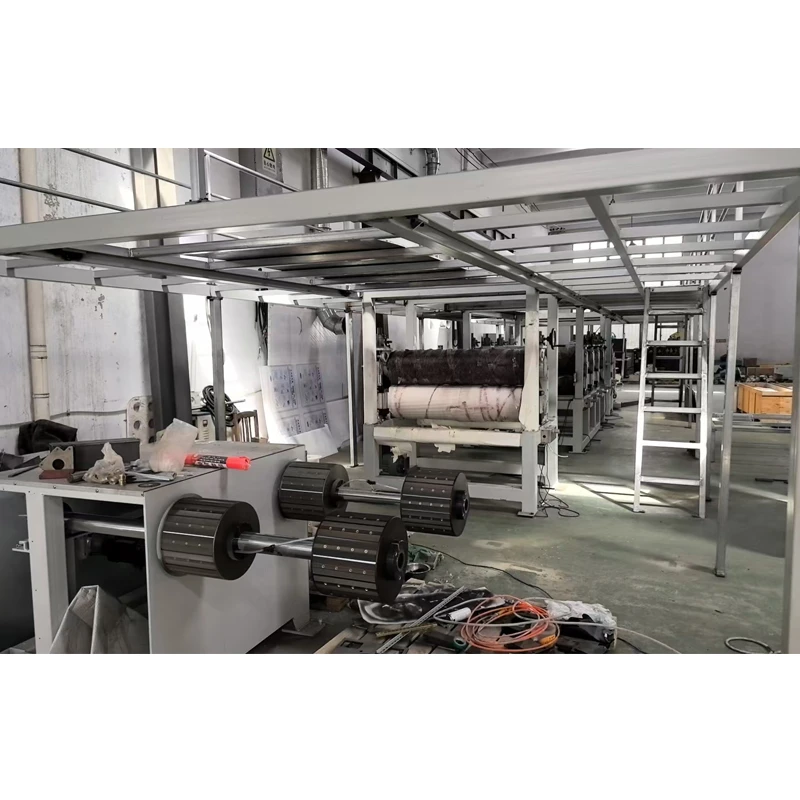
The transformation from traditional hand-operated looms to state-of-the-art automatic weaving machines is a testament to industrial ingenuity. The development of the Jacquard loom in the 19th century marked a pivotal point, enabling complex patterns through punched cards—an early example of programmable technology. By the mid-20th century, power looms with electrical and pneumatic controls became standard, slashing manual labor costs by over 70%. In recent decades, air jet and rapier looms have taken center stage, offering unprecedented speed and fabric quality.
Modern weaving machines can achieve speeds of up to 2,500 revolutions per minute (RPM), a tenfold increase over early mechanical looms. The integration of computer-aided design (CAD) allows rapid pattern changes, facilitating just-in-time manufacturing models. Furthermore, built-in sensors and IoT integration enable continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime by as much as 40%. The pace at which machine used for weaving fabric technology is evolving continues to reshape the capabilities and potential of textile production globally.
Comparing Leading Manufacturers: Global Market Analysis
Selecting the right weaving equipment hinges on understanding the landscape of leading machine manufacturers. Market leaders such as Toyota Industries, Picanol, Tsudakoma, Dornier, and Sulzer Texmach dominate the landscape, each offering distinct technological advantages.
| Manufacturer | Country | Key Technology | Max Weaving Speed (RPM) | Energy Efficiency (kWh/kg fabric) | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picanol | Belgium | Air Jet, Rapier | 2,100 | 0.80 | 19 |
| Toyota Industries | Japan | Water Jet, Air Jet | 2,300 | 0.75 | 18 |
| Tsudakoma | Japan | Air Jet | 2,500 | 0.82 | 15 |
| Dornier | Germany | Rapier, Air Jet | 2,000 | 0.87 | 13 |
| Sulzer | Switzerland | Projectile | 1,900 | 0.90 | 11 |
These data-driven insights allow textile producers to benchmark performance and assess operational costs before investment. While manufacturers vary in their technological focus, they collectively drive digital innovation and energy reduction efforts in the weaving sector.
Custom Solutions: Tailoring Weaving Machines to Industry Needs
The market is no longer one-size-fits-all—machine used for weaving solutions are extensively customizable. Producers can specify loom dimensions, accommodate specialized yarns (such as carbon fiber or metallic threads), or integrate hybrid technologies suited for diverse end products. Some companies require ultra-high-density weaving for technical fabrics, while others prioritize flexible configuration for fashion textiles.
Automation options now include robotic yarn change, adaptive tension controls, and bespoke software modules for real-time quality management. This level of customization means that productivity can increase by up to 30% with properly tailored equipment. Leading vendors offer modular upgrades, allowing manufacturers to add advanced features without full system replacement, supporting sustainable investments and long-term scalability.
Applications and Real-World Case Studies
The reach of modern weaving machines extends across numerous industries beyond traditional garment fabrics. For example, Stäubli’s advanced Jacquard machines are instrumental in producing complex automotive textiles, which must meet rigorous safety and durability standards. In fact, the global market for technical textiles, which includes products like airbags and geotextiles, surpassed $175 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow by 6% annually.
Another notable application is in medical textiles: woven pacemaker lead sheaths and surgical mesh are produced on precision weaving machines with deviations of less than 0.01 mm. In aerospace, carbon fiber looms supply high-strength reinforcement fabrics essential for lightweight, high-performance components. Success stories from leading textile mills consistently report a reduction in fabric defects of at least 15% after upgrading to digitally enhanced weaving systems, directly contributing to competitive advantage and faster market entry.
Performance Metrics: A Data-Driven Overview of Weaving Efficiency
Quantifying performance is essential to justify investment in a new machine used for weaving fabric. Key performance indicators (KPIs) include cycle time, energy consumption, defect rates, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). For instance, air jet looms average 2,000-2,300 picks per minute, while power consumption ranges from 0.70–0.90 kWh per kilogram fabric, depending on machine type and automation level.
Across a sample of 100 weaving mills worldwide, recent benchmarking studies show average fabric wastage rates fell from 7% (legacy systems) to under 4% post-adoption of modern weaving solutions. Digital sensors and predictive maintenance platforms not only reduce machine downtime by up to 40%, but also increase fabric quality consistency by more than 10%. An optimized weaving process can bring average lead times for fabric orders down from 14 days to less than 6 days, which translates into significant cost savings and market responsiveness.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of the Machine Used for Weaving
In summary, the machine used for weaving is fundamental to progress in textiles, enabling manufacturers to push boundaries in speed, precision, and sustainability. Understanding the technical landscape, performance metrics, and custom capabilities ensures that industry professionals select the most suitable solution for their operations. With global demand for high-quality, diversified woven products on the rise, investing in advanced weaving machines has become a critical differentiator for success. As technology continues to evolve, the potential of weaving machinery to deliver intelligent, efficient, and innovative fabric solutions shows no signs of slowing down.

(the machine used for weaving)
FAQS on the machine used for weaving
Q: What is the machine used for weaving?
A: The machine used for weaving is called a loom. Looms interlace two sets of threads to create fabric. They come in manual and automatic varieties.
Q: Which machine is used for weaving fabric in industries?
A: In industries, weaving fabric is typically done on power looms. These machines are faster and more efficient than handlooms. Power looms can produce large quantities of fabric.
Q: Is there a specific machine used for weaving?
A: Yes, the loom is specifically designed for weaving. It holds the warp threads taut so the weft can be woven through. Different types of looms exist for various weaving needs.
Q: What are the main types of machines used for weaving?
A: The main types are handlooms, power looms, and automatic looms. Each serves different production purposes. Selection depends on size and complexity of the fabric.
Q: How does a machine used for weaving work?
A: A weaving machine passes weft threads over and under taut warp threads. This process creates woven fabric. Modern looms automate much of this process for efficiency.
Następny