- Fundamentals of Weaving Machines
- Manufacturing Process and Requirements
- Operational Mechanics Explained
- Practical Operational Guidelines
- Performance Advantages and Data Metrics
- Industry-Leading Manufacturer Comparison
- Implementation Strategies and Future Innovations

(what is a weaving machine)
Understanding What Is a Weaving Machine
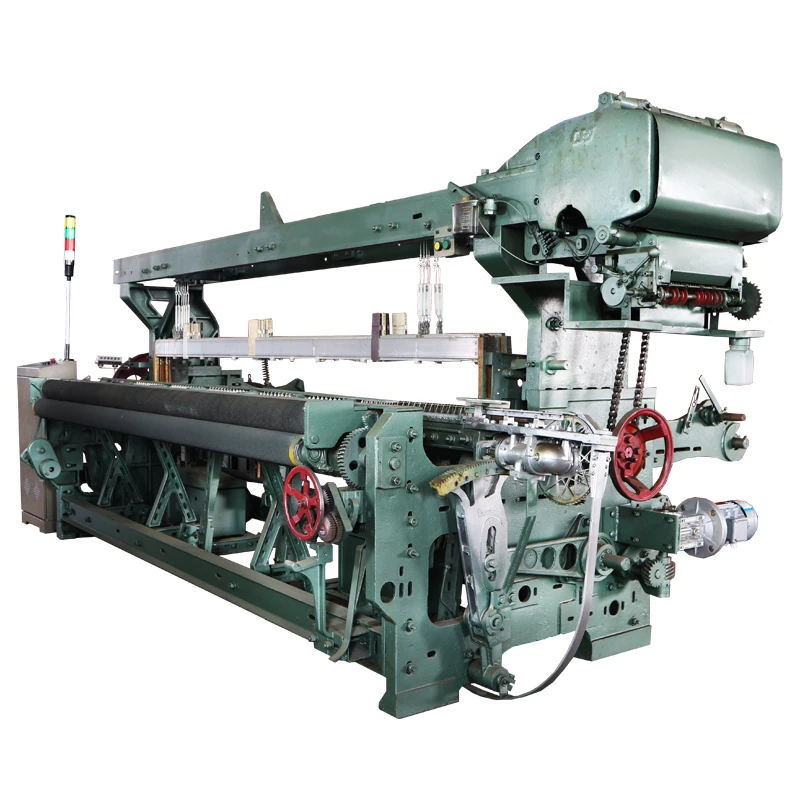
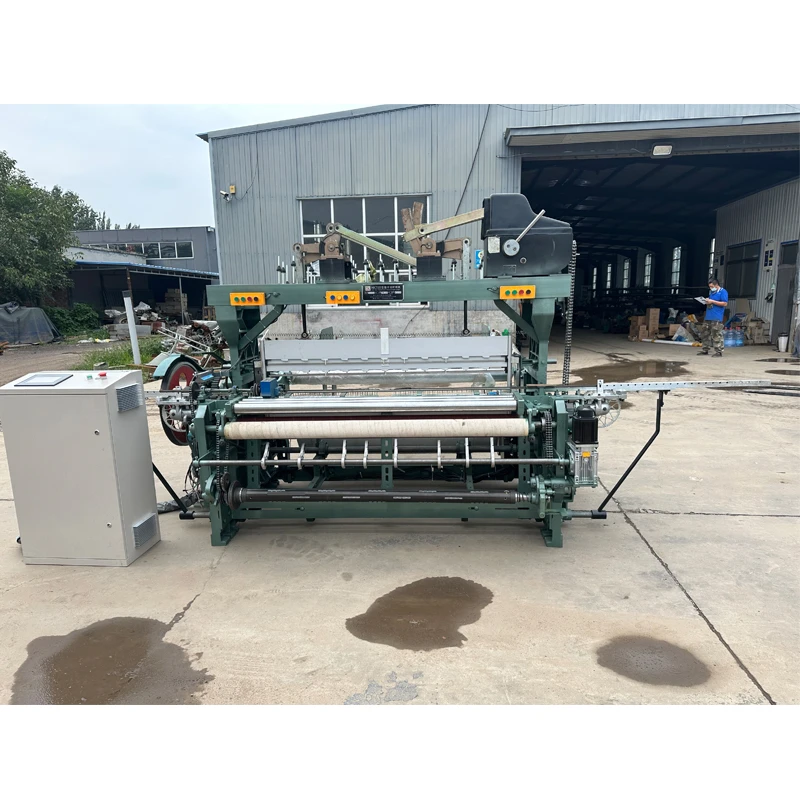
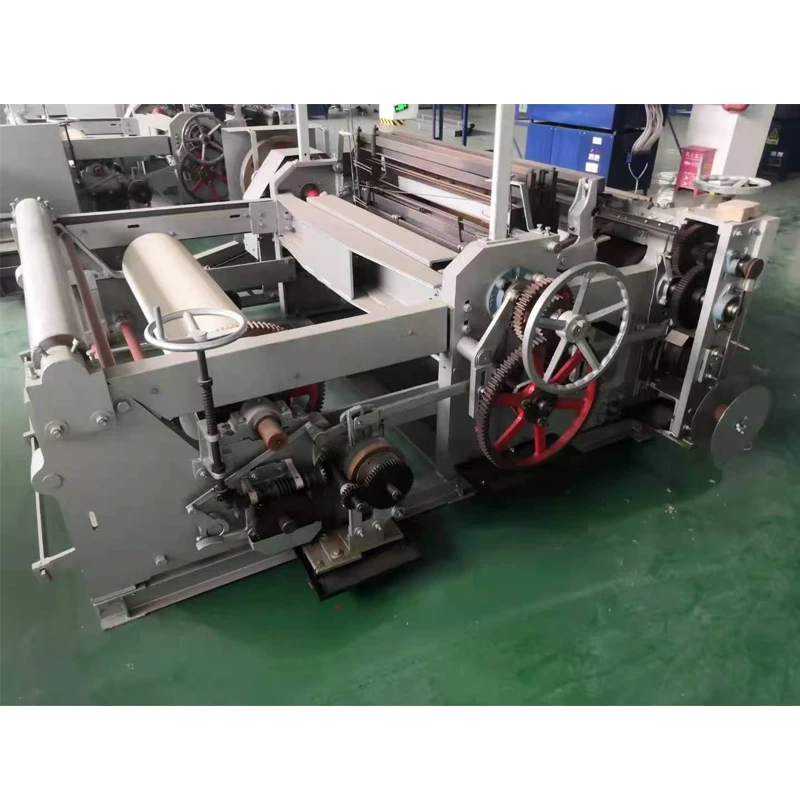
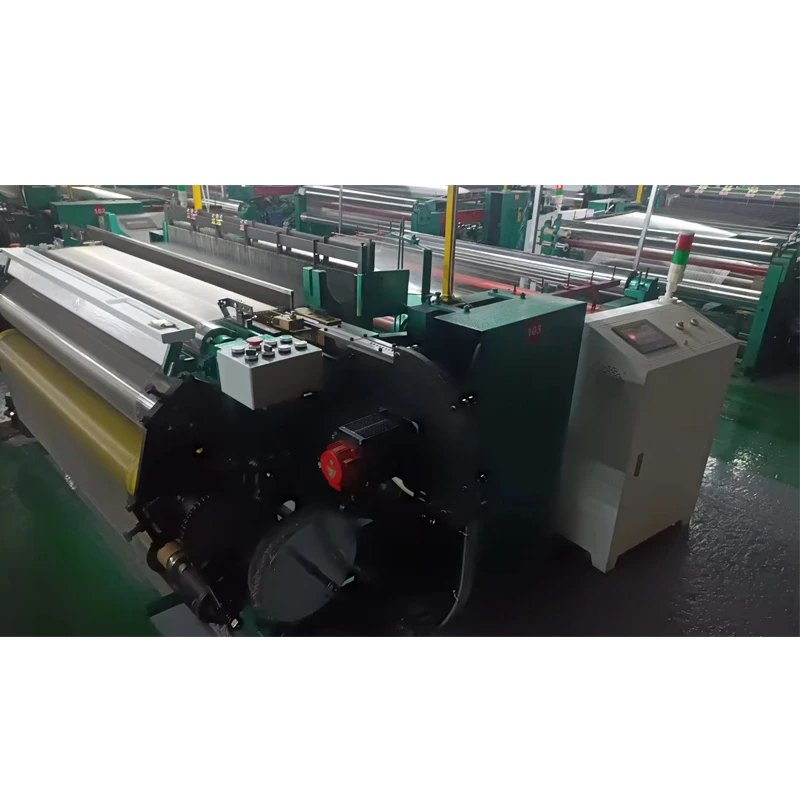
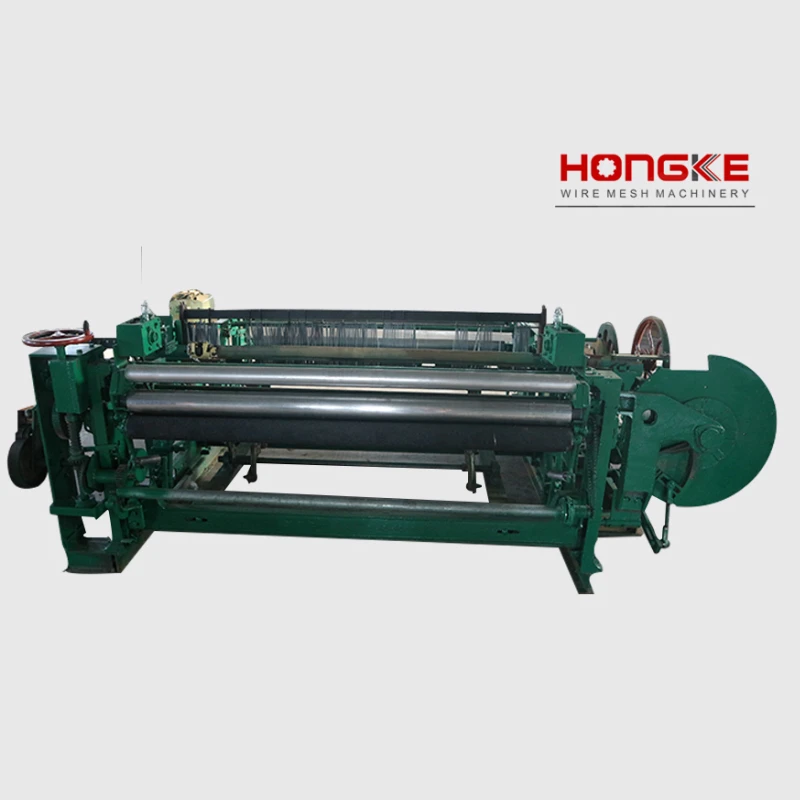
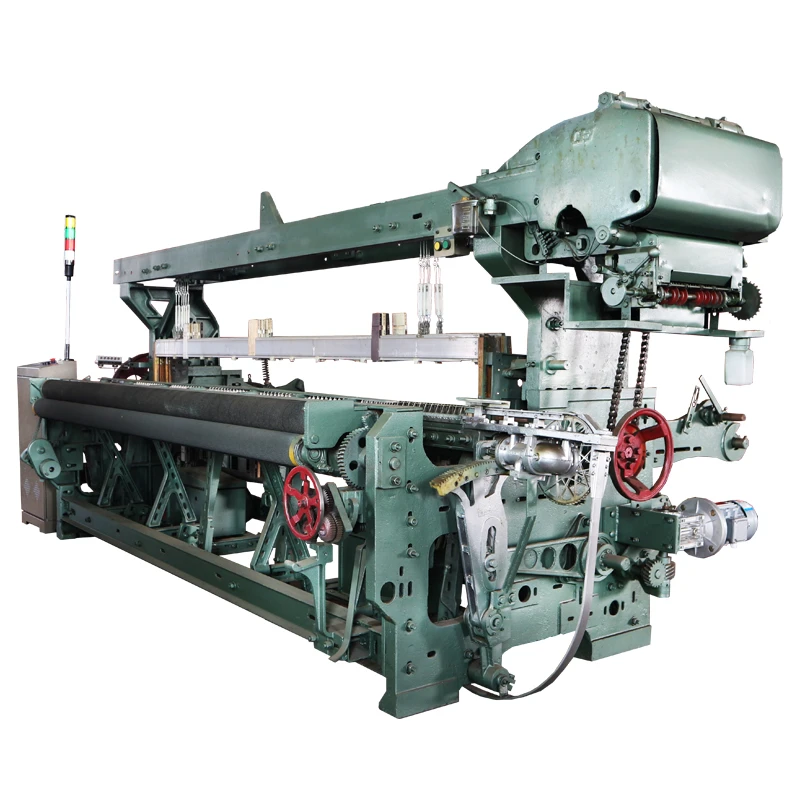
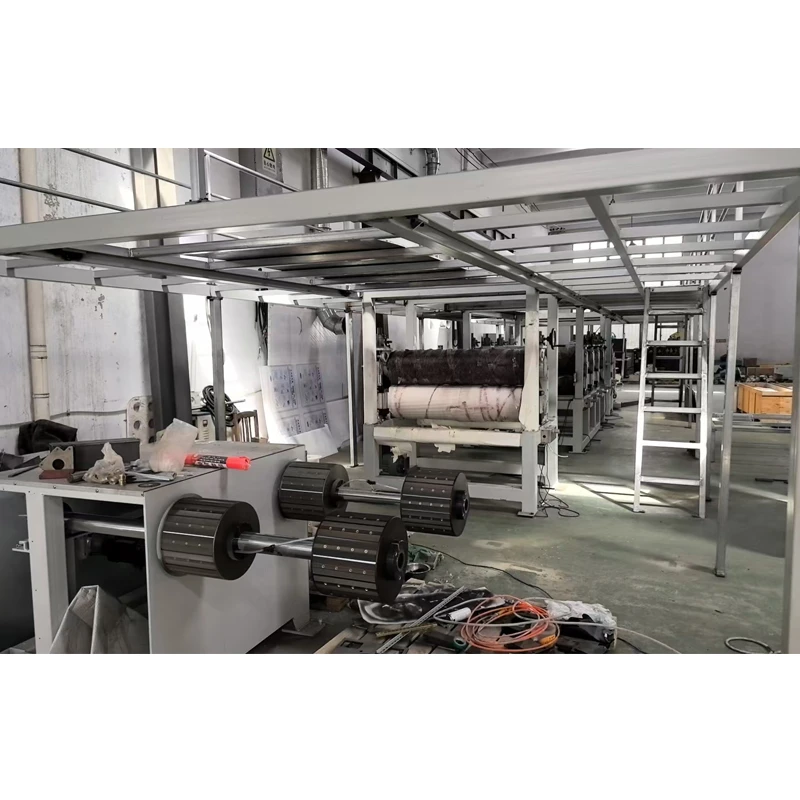
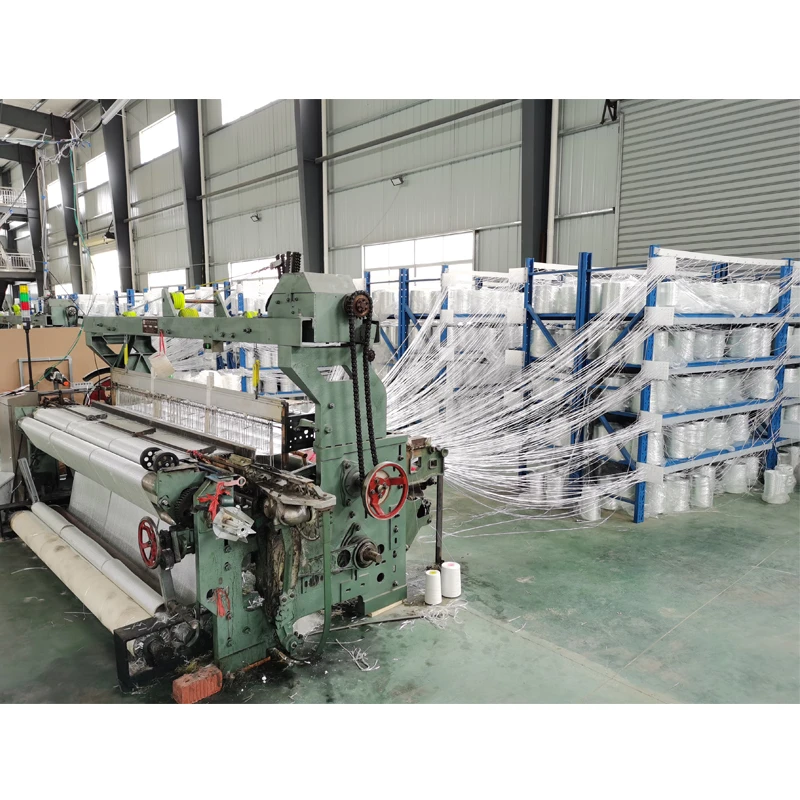
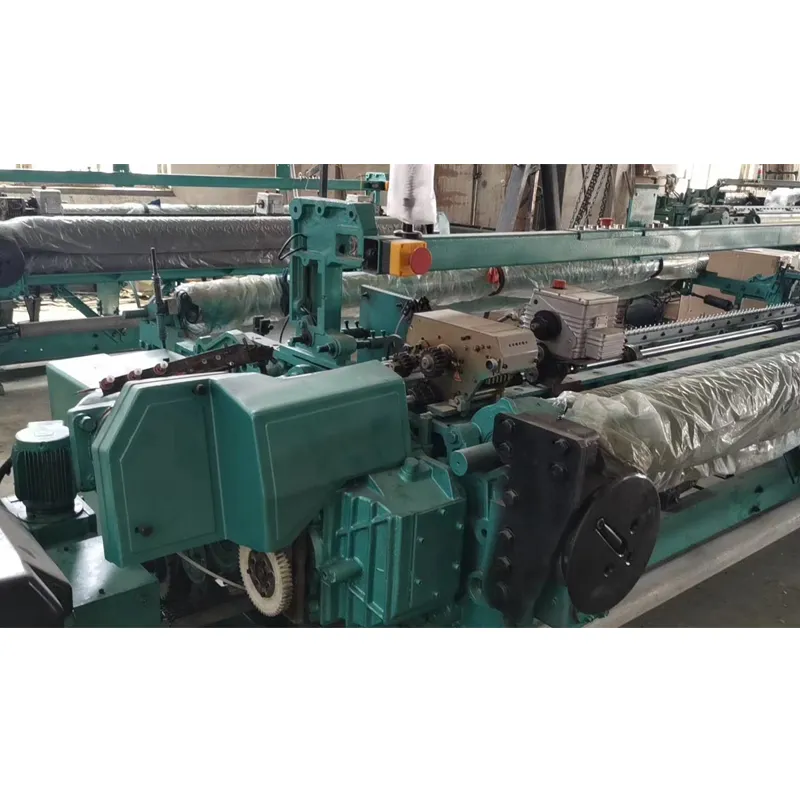
At its core, a weaving machine interlaces longitudinal warp threads with horizontal weft threads to produce fabric. Modern variants like rapier, air-jet, and projectile looms have evolved from traditional handlooms, achieving speeds exceeding 2,000 picks per minute (ppm). The textile industry relies on these machines for 95% of global fabric production, with automated models reducing labor costs by 60% compared to manual alternatives. Key subsystems include warp beams, heddles, reeds, and shedding mechanisms that collectively enable continuous material formation without manual intervention.
How to Make Weaving Machine Components
Manufacturing industrial weaving equipment requires precision engineering and specialized materials. Critical steps include:
Frame Fabrication: Laser-cut steel components undergo CNC machining for ±0.05mm tolerances before robotic welding creates vibration-resistant structures.
Motion Systems: Cam shedding mechanisms are hardened to 60 HRC for 100,000+ operating hours, while carbon-fiber rapiers withstand 10G acceleration forces during shuttle-less operation.
Electronic Integration: Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) with IoT sensors monitor 120+ operational parameters like tension (0-500N adjustability) and temperature.
Facilities implementing Industry 4.0 techniques report 30% faster assembly times through automated calibration benches that verify alignment within 5-micron specifications.
How Weaving Machine Works Technically
Fabric formation occurs through five synchronized phases:
- Shedding: Heddles separate warp threads into layers, creating triangular openings for weft insertion
- Picking: Compressed air (6-10 bar pressure) propels weft yarns through the shed at 40m/second velocity
- Beating: Reed combs compress weft threads at 150-400 beats/minute into the fell line
- Let-off: Servo motors unwind warp beams with 0.1mm precision to maintain constant tension
- Take-up: Finished fabric rolls onto cloth beams at rates up to 100cm/minute
Closed-loop feedback systems using encoders correct positional errors within 5 milliseconds, achieving 99.3% production accuracy.
How to Use Weaving Machine Efficiently
Maximizing operational efficiency involves systematic protocols:
Setup Phase: - Warp threading requires 35-90 minutes depending on complexity (pattern density between 10-120 threads/cm) - Air pressure calibration must maintain ±0.2 bar accuracy for consistent weft insertion
Runtime Management: - Lubrication cycles every 400 operating hours extend bearing lifespan by 200% - Real-time RPM adjustments via touchscreen interfaces optimize energy consumption (typical range: 450-650 RPM) - Automatic broken thread detection halts operations in <0.5 seconds to minimize waste
Operators trained in predictive maintenance reduce unplanned downtime by 55% through vibration analysis and thermal imaging protocols.
Technical Advancements by Metrics
Modern looms demonstrate measurable superiority over legacy systems:
| Performance Parameter | Mechanical Looms | Automated Variants | % Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed (ppm) | 150-300 | 600-2,000 | 550% |
| Fabric Defects/100m | 8-12 | 0.3-1.2 | 88% |
| Energy Consumption (kWh/m) | 0.48 | 0.19 | 60% |
| Changeover Time | 120-180 min | 15-25 min | 86% |
These enhancements translate to 23% higher fabric yield and 40% reduced labor costs per production unit.
Manufacturer Capabilities Analysis
Leading brands differentiate through specialized engineering:
| Manufacturer | Peak Speed (ppm) | Max. Width (cm) | Smart Features | Output (m²/hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picanol OMNIplus | 1,250 | 540 | AI defect detection | 82 |
| Dornier P1 | 1,100 | 380 | Cloud connectivity | 67 |
| Toyota JAT810 | 950 | 220 | Automatic recipe recall | 58 |
| Tsudakoma ZAX | 1,400 | 460 | Predictive maintenance | 91 |
High-output models now incorporate machine learning algorithms that increase weaving precision by analyzing 200,000+ weave patterns monthly.
Customizing What Is a Weaving Machine for Tomorrow
Adaptive configurations enable specialized applications:
Medical Textiles: Jacquard attachments create complex vascular graft patterns with <10µm precision while maintaining sterile environments.
Aerospace Solutions: Carbon fiber weaving machines produce reinforced composites with 160N/tex tensile strength for aircraft components.
Smart Textiles: Conductive thread integration creates fabrics with embedded sensors, enabling biometric monitoring during the weaving process itself.
Future innovations include nanotechnology coatings that reduce yarn friction by 75% and quantum computing integration that optimizes pattern complexity in real-time, projected to increase production efficiency by 35% by 2028.

(what is a weaving machine)
FAQS on what is a weaving machine
以下是围绕指定关键词创建的5组FAQs问答,采用HTML富文本格式:Q: What is a weaving machine?
A: A weaving machine (or loom) is a device that interlaces longitudinal warp threads and horizontal weft threads to create fabric. It automates the traditional hand-weaving process for efficient textile production. Modern versions include computer-controlled industrial looms.
Q: How does a weaving machine work?
A: It works by raising/lowering warp threads to form a "shed" opening. A shuttle or rapier then inserts the weft thread through this opening. The reed beats the weft against the formed fabric, repeating this process row by row.
Q: How to use a basic weaving machine?
A: First, thread the warp yarns through heddles and the reed. Next, load the weft yarn onto a shuttle and start the machine. Maintain consistent tension and monitor for broken threads during operation.
Q: Can I build a simple weaving machine at home?
A: Yes, create a frame loom using wooden bars and nails. Space nails ¼ inch apart on top/bottom bars to hold warp threads. Add a removable shed stick to alternate thread layers for manual weft insertion.
Q: What are key weaving machine maintenance steps?
A: Regularly clean lint buildup from reeds and shuttle tracks. Check and oil moving parts like the batten and heddles according to manufacturer guidelines. Always replace worn components like heddle eyes promptly.
说明: 1. 每组FAQ包含一个``标题标签的问题(前缀Q:) 2. 回答使用`
`段落标签(前缀A:) 3. 每组严格控制在3句以内 4. 包含所有指定关键词:基本定义(what)、工作原理(how it works)、使用方法(how to use)和制作方法(how to make) 5. 第五组聚焦维护实践,属于"how to use"的延伸应用 6. 使用``标签突出Q/A标记确保可读性
E kaluara
Tjetra