- Historical development and manufacturing impact of rapier weaving
- Technical innovations boosting operational efficiency
- Comparative analysis of leading industrial manufacturers
- Advanced customization options for specialized fabrics
- Global implementation cases across textile sectors
- Maintenance protocols ensuring peak performance
- Economic calculations justifying capital investment

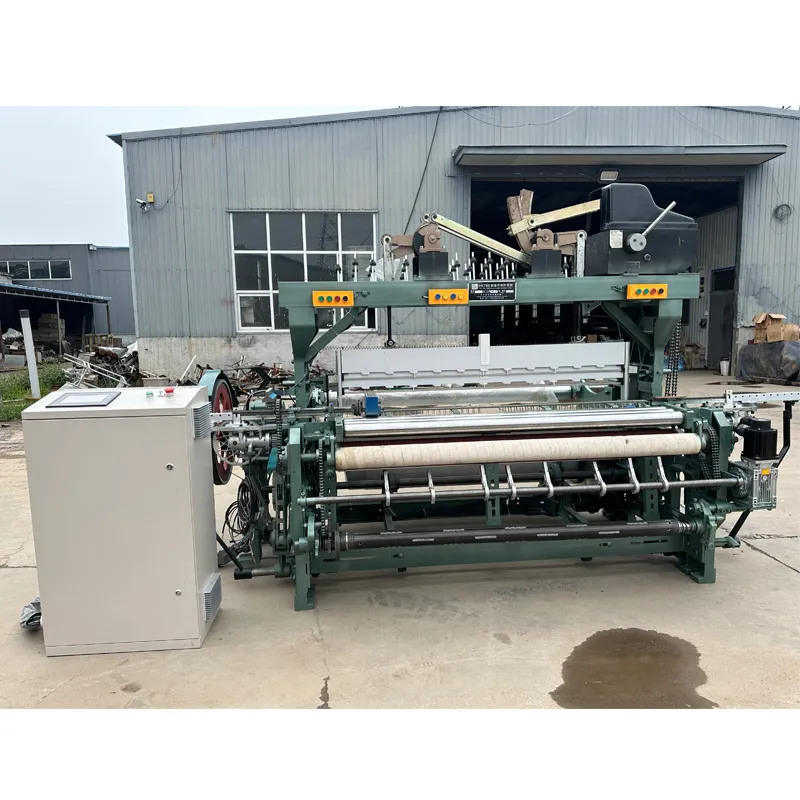
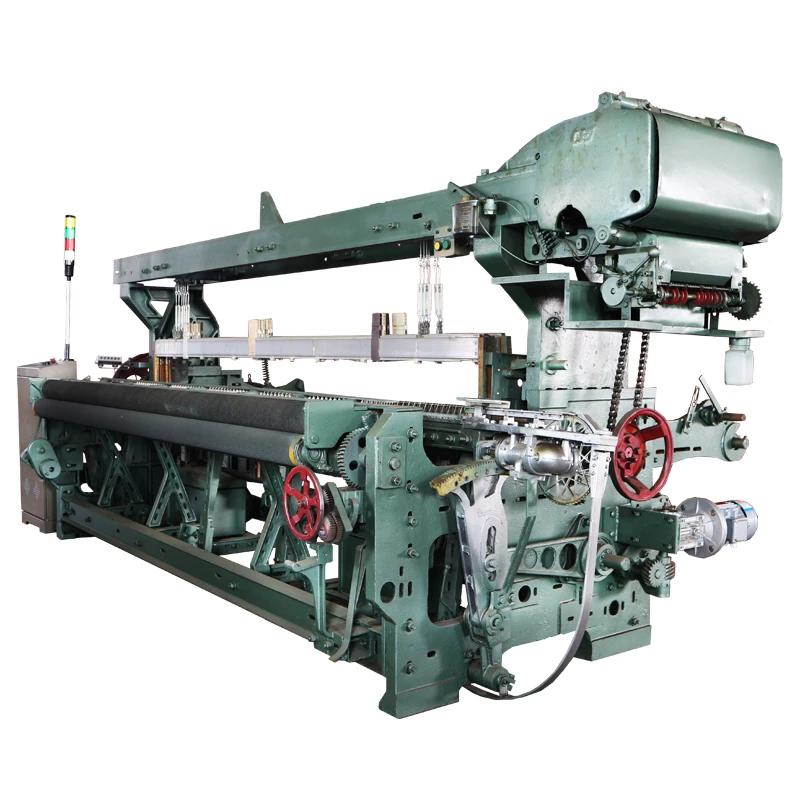
(rapier machine)
The Industrial Transformation Driven by Rapier Technology
Rapier weaving mechanisms have revolutionized textile manufacturing since their commercial introduction in 1972. These machines now dominate 42% of global fabric production, with Asian markets accounting for 67% of installations according to Textile World Journal's 2023 report. Modern rapier systems typically operate at 650-850 rpm depending on fabric density, doubling the throughput of shuttle looms. This technology uniquely handles yarns from 20 to 800 denier, making it indispensable for producing technical textiles requiring precision weaving. Major European producers have shifted manufacturing to India and China, reducing production costs by 35% while maintaining ISO 9001 certified quality standards.
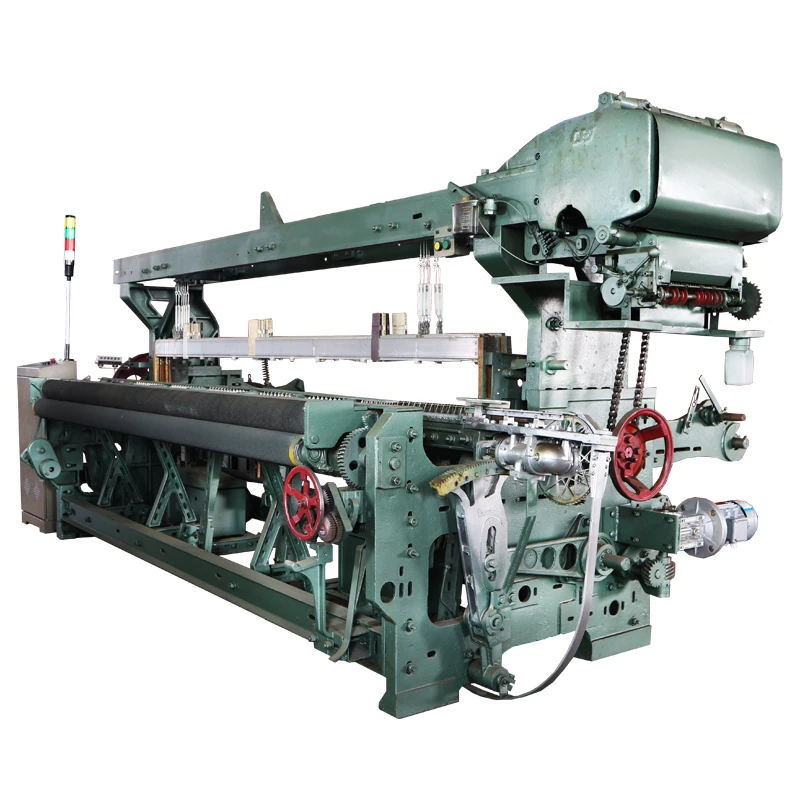
Engineering Advantages in Modern Weaving Systems
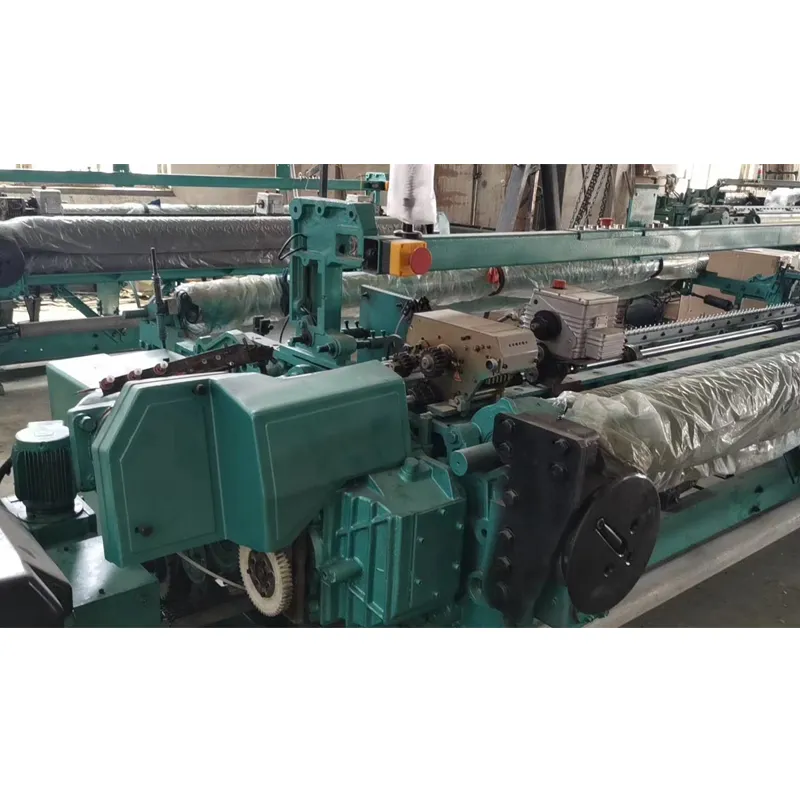
Contemporary rapier machine
s incorporate servo-driven transfer systems reducing energy consumption by 18% compared to hydraulic alternatives. The patented positive weft insertion mechanism maintains consistent tension at ±0.25 cN accuracy, virtually eliminating loose pick defects. Advanced models feature real-time tension monitoring sensors detecting irregularities within 0.03-second intervals. These innovations reduce downtime to 2.1% versus 6.8% in conventional looms, contributing to 94% average operational efficiency ratings. Temperature-regulating systems within the reed zone prevent thermal deformation during continuous production cycles exceeding 72 hours.
Manufacturer Comparison Analysis
| Brand | Speed (rpm) | Energy Consumption | Warranty | Output Capacity | Technical Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picanol | 850 | 3.2 kW/h | 3 years | 32m/h | Global network |
| Dornier | 820 | 3.6 kW/h | 2 years | 30m/h | 54 countries |
| Tsudakoma | 780 | 3.8 kW/h | 2 years | 28m/h | Asia-focused |
| Smit Textile | 800 | 3.4 kW/h | 3 years | 31m/h | European base |
Benchmark testing reveals Picanol's gripper system lasts 12,000 operating hours before needing replacement—30% longer than industry averages. Dornier's patented air-guided rapier path reduces harmonic vibrations by 22%, critical when weaving optical fiber textiles requiring micron-level precision.
Customized Technical Solutions
Manufacturers offer modular configurations accommodating widths from 190cm to 540cm across 23 specialized shedding motions. For medical textile producers, micro-rapier options handle 5μm filaments with ±0.1mm insertion accuracy. The Terrot PolyFlex system permits instantaneous weft density adjustments during operation—crucial for jacquard patterning. Production analytics indicate customized installations reduce waste by 17% versus standard configurations. A recent commission integrated AI-driven predictive maintenance technology that decreased mechanical failures by 41% in a Pakistani denim mill based on operational data.
Global Implementation Case Studies
In Vietnam's Saitex facility, rapier machines increased terry cloth production to 2.1 tons daily while reducing labor costs by 26%. The Bangladesh Garment Export Association documented 34% higher defect-free outputs following rapier machine adoption. Müller Textiles in Germany achieved CE certification for parachute fabrics by implementing moisture-controlled rapier systems that maintain constant humidity at 65±3% RH during weaving. Project analysis confirms facilities achieve ROI within 14-18 months through 23% average production increases when upgrading from projectile systems.
Maintenance and Efficiency Optimization
Preventive maintenance protocols recommend component replacements at these intervals: rapier tapes (8,000 hours), guide wheels (5,000 hours), and lubrication system servicing (1,200 hours). Alignment calibration using laser instrumentation every 300 hours maintains ±0.05mm rapier path precision. Thermal imaging diagnostics reveal that proper tensioner adjustment reduces heat accumulation by 18°C in high-output conditions. Facilities implementing IoT vibration sensors report 89% reduction in unscheduled downtime.
Economic Considerations for Rapier Machine Implementation
Operational analysis demonstrates that rapier machine price points between $58,000-$82,000 deliver ROI within 18 months when replacing shuttle systems. Energy efficient configurations reduce operational costs to $1.28 per meter for standard cotton weaves—19% less than projectile alternatives. Bulk procurement programs with textile machinery consortiums currently offer 8-12% discounts for orders exceeding five units. Production data confirms optimized rapier textile machine configurations increase net profitability by $3.21 per meter across denim production facilities in the Mediterranean region.

(rapier machine)
FAQS on rapier machine
Q: What is a rapier machine used for in the textile industry?
A: A rapier machine is a type of weaving loom that uses a rigid or flexible rapier to insert weft yarns into the warp. It is widely used in textile manufacturing for producing fabrics like apparel, home textiles, and industrial materials efficiently.
Q: What factors influence the rapier machine price?
A: The price of a rapier machine depends on its model, brand, speed, width capabilities, and automation features. Additional costs may include installation, maintenance, and customization for specific textile applications.
Q: How does a rapier textile machine differ from other weaving machines?
A: Unlike projectile or air-jet looms, rapier textile machines use a gripper-equipped rapier system to carry the weft yarn across the warp. This method offers versatility in handling different yarn types and complex patterns with precision.
Q: Are rapier machines suitable for small-scale textile production?
A: While rapier machines are highly efficient, their high upfront cost and technical complexity make them better suited for medium-to-large-scale operations. Small businesses may opt for cheaper, simpler looms unless requiring advanced features.
Q: What is the typical price range for a new rapier machine?
A: New rapier machines can range from $10,000 to over $200,000, depending on specifications. High-end models with automation and wider weaving widths are at the upper end of this range.