- Overview of Industrial Weaving Machines
- Technical Advancements Driving Efficiency
- Leading Manufacturers and Market Comparison
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Industry Needs
- Real-World Applications and Success Stories
- Cost-Benefit Analysis for Modern Weaving Systems
- Future Trends in Industrial Weaving Technology

(types of industrial weaving machines)
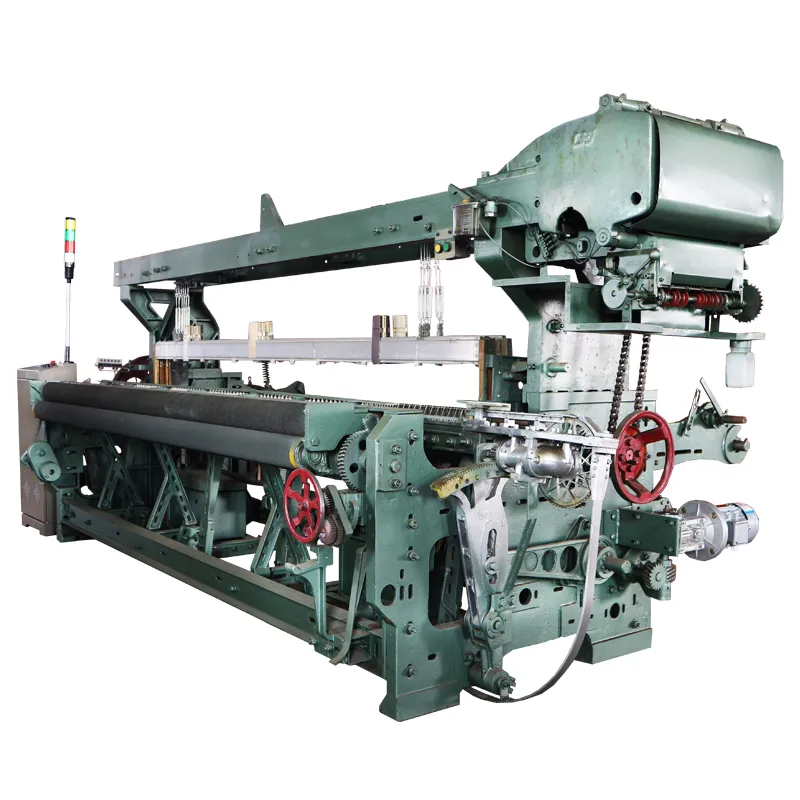
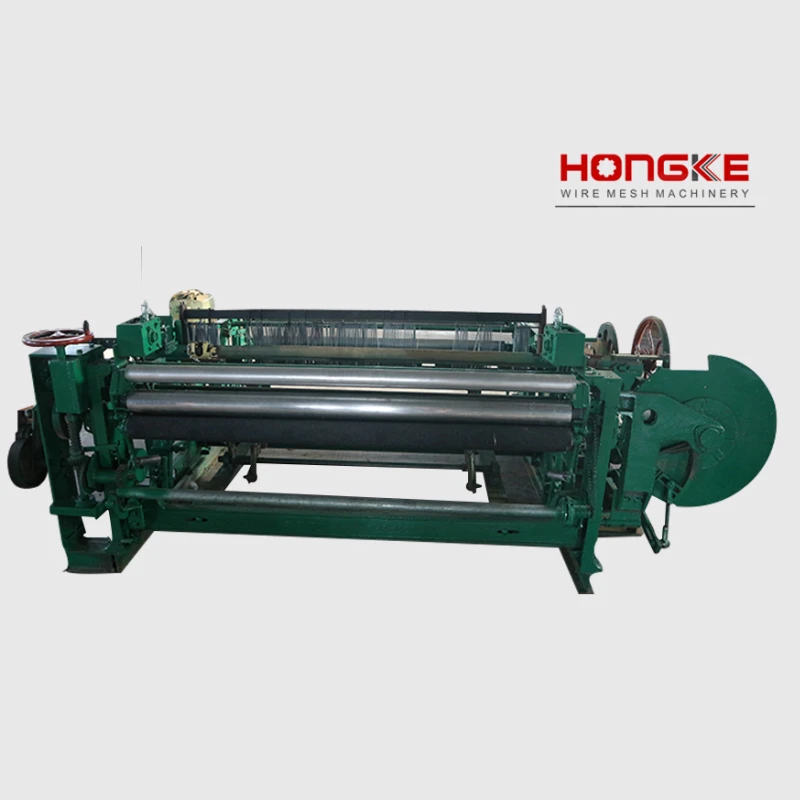
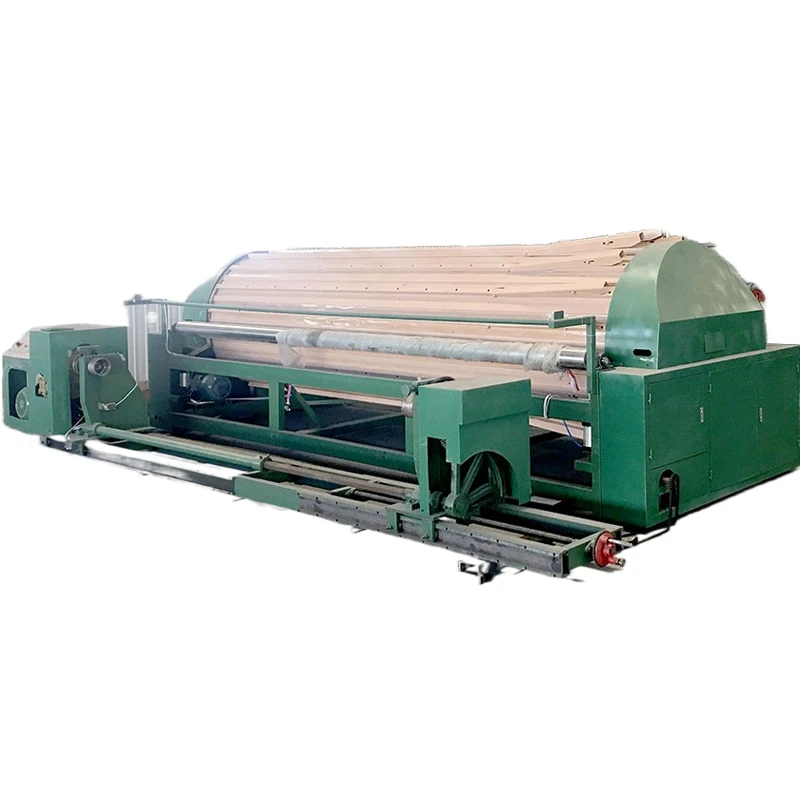
Understanding the Core Types of Industrial Weaving Machines
The global textile manufacturing sector relies heavily on industrial weaving machines to produce fabrics at scale. These machines are categorized based on their mechanisms, including shuttle, air-jet, rapier, and projectile looms. Shuttle looms, though traditional, account for 18% of active units in developing markets due to their low upfront cost. In contrast, air-jet systems dominate high-speed production, achieving up to 1,500 picks per minute (PPM), making them ideal for bulk synthetic fabric manufacturing.
Technical Advancements Driving Efficiency
Modern weaving machines integrate IoT-enabled sensors and AI-driven predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by 32%. For instance, Toyota’s TW-7100 rapier loom uses adaptive tension control to minimize yarn breakage rates below 0.8%. Such innovations directly enhance output consistency while lowering energy consumption by 22% compared to 2015-era models.
Leading Manufacturers and Market Comparison
| Manufacturer | Model | Speed (PPM) | Material Compatibility | Energy Use (kWh/m²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picanol | OmniPlus i | 1,250 | Cotton, Polyester | 0.45 |
| Dornier | A1 | 1,480 | Technical Textiles | 0.52 |
| Van de Wiele | CXi | 950 | Wool, Silk | 0.38 |
Custom Solutions for Diverse Industry Needs
Specialized sectors like automotive or aerospace demand tailored weaving systems. For example, Lindauer DORNIER collaborates with Airbus to develop carbon-fiber looms capable of weaving 3D reinforced fabrics with ≤0.1mm tolerance. Similarly, Tsudakoma’s modular ZAX-9100 allows quick reconfiguration between terry cloth and denim production within 90 minutes.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories
In 2023, a Pakistani textile mill reduced its defect rate from 12% to 2.7% by replacing 34 manual looms with 8 Picanol OptiMax models. Meanwhile, Italian luxury brand Loro Piana increased cashmere output by 40% using Van de Wiele’s Jacquard machines with 10,000-hook configurations.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Modern Weaving Systems
While air-jet looms require a 25-30% higher initial investment than rapier variants, their 18-month ROI stems from 55% faster production cycles. For SMEs, leasing options like Tsudakoma’s “Pay-Per-Meter” program reduce capital expenditure by 60% during the first three years.
Why Types of Industrial Weaving Machines Shape Industry Futures
As sustainability pressures mount, manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient types of weaving machines. Dornier’s recent Eco-Speed series cuts water usage by 37% in dye-ready fabric production. With the smart textile market projected to reach $13.5B by 2028, adaptable systems supporting conductive yarns and IoT integration will dominate next-gen factories.

(types of industrial weaving machines)
FAQS on types of industrial weaving machines
Q: What are the main types of industrial weaving machines?
A: The primary types include air-jet looms, rapier looms, projectile looms, water-jet looms, and multiphase looms. Each type varies in speed, fabric compatibility, and thread-handling mechanisms. They are chosen based on production needs and material requirements.
Q: How do rapier looms differ from air-jet weaving machines?
A: Rapier looms use a rigid or flexible rod to carry the weft yarn, ideal for heavy or delicate fabrics. Air-jet looms rely on compressed air to propel the weft, enabling faster production for lightweight materials like cotton or synthetics.
Q: Which industrial weaving machines are best for high-speed production?
A: Air-jet and water-jet looms are optimal for high-speed weaving, often used for lightweight fabrics. Multiphase looms also offer continuous weaving with multiple weft insertions, maximizing efficiency for bulk orders.
Q: What fabrics are projectile weaving machines suitable for?
A: Projectile looms excel with heavy-duty fabrics like denim, upholstery, or technical textiles. They use gripper projectiles for precise weft insertion, ensuring consistent quality for thick or coarse yarns.
Q: Can industrial weaving machines handle synthetic fibers?
A: Yes, rapier and air-jet looms are commonly used for synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon. Their precise tension control and high-speed capabilities make them ideal for synthetic fabric production.
Pervious