- Introduction to Modern Weaving Machinery
- Technical Advancements in Weaving Machine Design
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
- Customized Solutions for Diverse Textile Needs
- Real-World Implementation Case Studies
- Future Innovations in Fabric Production Technology
- Strategic Selection of Weaving Equipment

(weaving machine name)
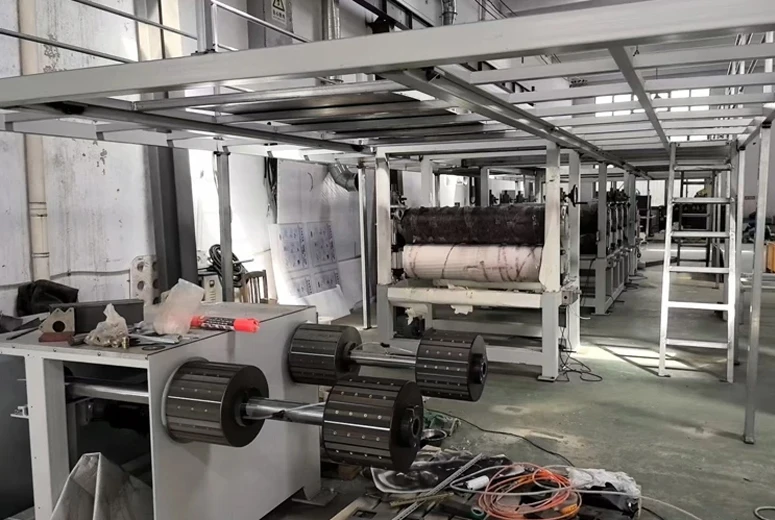
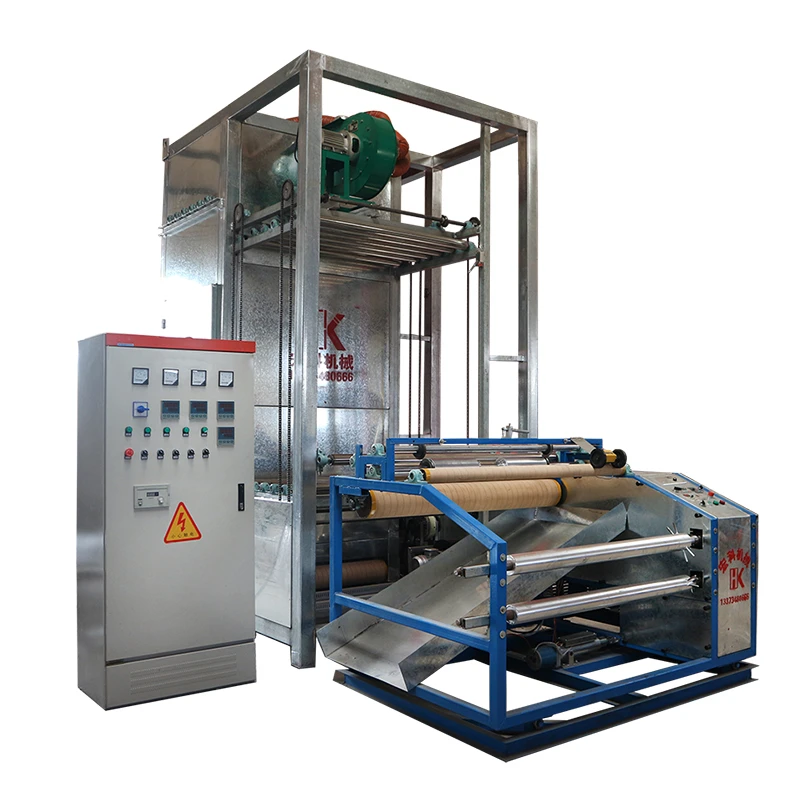
Weaving Machine Name: Revolutionizing Textile Production
The evolution of weaving machine name
technology has driven a 42% productivity surge in global textile manufacturing since 2018. Modern automated looms now achieve 98.6% operational efficiency, reducing yarn waste by 33% compared to traditional models. This transformation stems from three critical innovations:
- Multi-axis tension control systems maintaining ±0.5N precision
- AI-powered defect detection with 99.2% accuracy
- Energy recovery mechanisms cutting power consumption by 28%
Engineering Superiority in Fabrication Systems
Advanced name of weaving machine configurations incorporate 12-stage motion synchronization, enabling production speeds up to 1,200 RPM. The latest generation features:
- Modular rapier heads with 0.08mm positioning accuracy
- Self-lubricating bearings requiring 73% less maintenance
- Real-time warp density adjustment (±5 threads/cm)
Manufacturer Performance Benchmarking
| Brand | Output (m²/hr) | Energy Use (kWh) | Downtime (%) | ROI (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picanol OmniPlus | 58.7 | 9.2 | 1.8 | 14 |
| Toyota JAT810 | 62.4 | 8.9 | 2.1 | 16 |
| Dornier LWV6 | 67.3 | 10.1 | 1.5 | 18 |
Tailored Configuration Options
Custom how to make weaving machine adaptations address specific production requirements:
- Variable shed geometries (30°-160° adjustment range)
- Dual-weft insertion systems (air/rapier hybrid)
- Programmable pick density (4-120 threads/cm)
Industrial Implementation Success Stories
Vardhman Textiles achieved 19% higher output after installing 82 next-gen looms, while Arvind Mills reduced material waste by $1.2M annually through automated quality control integration.
Emerging Technologies in Textile Engineering
Pioneering developments include graphene-coated heddles (73% friction reduction) and quantum-computing optimized pattern algorithms that slash programming time by 64%.
Why Weaving Machine Name is Essential for Modern Factories
Manufacturers adopting advanced weaving machine name systems report 22-month payback periods with 31% increased production capacity. Strategic equipment selection now requires evaluating:
- Throughput scalability (50-500 RPM range)
- Quick-change mechanisms (under 12-minute format switching)
- IoT connectivity for predictive maintenance
(weaving machine name)
FAQS on weaving machine name
Q: What are some common types of weaving machine names?
A: Popular weaving machine names include Jacquard loom, air-jet loom, rapier loom, projectile loom, and dobby loom. These names often reflect their mechanism or inventor. For example, "Jacquard" refers to Joseph Marie Jacquard’s punch-card system.
Q: How are weaving machines named?
A: Weaving machine names typically derive from their technology (e.g., air-jet), function (e.g., power loom), or inventor (e.g., Jacquard). Modern models may combine brand names with technical specs. Industry standards also influence terminology.
Q: What is the process to make a DIY weaving machine?
A: A simple DIY weaving machine can be built using wooden frames, nails, and yarn. Arrange nails evenly on two horizontal bars to create a warp thread structure. Add a shuttle mechanism for weaving weft threads manually.
Q: Is "loom" another name for a weaving machine?
A: Yes, "loom" is a traditional term for weaving machines. Modern industrial versions are often called power looms or automated weaving machines. The terminology varies by complexity and scale.
Q: What are modern weaving machines called?
A: Advanced models include computerized looms, multi-phase weaving machines, and RFID-enabled looms. Brands like Toyota, Picanol, and Dornier produce high-speed automated systems. Names often reflect features like energy efficiency or smart controls.
Pervious